ERC-7857: Standard untuk Intelligent NFT
ERC-7857 adalah standar NFT baru yang memperluas ERC-721 dengan kemampuan untuk menyimpan dan mengelola metadata terenkripsi, memungkinkan transfer kepemilikan yang aman untuk aset AI.
Overview
Mengapa Butuh Standard Baru?
ERC-721 tradisional memiliki keterbatasan:
| Limitasi ERC-721 | Solusi ERC-7857 |
|---|---|
| Metadata publik | Encrypted metadata |
| Tidak ada mekanisme re-encrypt | Secure re-encryption on transfer |
| Tidak ada verification | Oracle-based verification |
| Tidak ada usage control | Built-in authorization system |
Core Features ERC-7857
- Encrypted Metadata - AI configurations tersimpan terenkripsi
- Secure Re-encryption - Data di-re-encrypt saat transfer
- Oracle Verification - Third-party memverifikasi legitimacy
- Authorized Usage - Sistem rental/license built-in
Alur Kerja ERC-7857
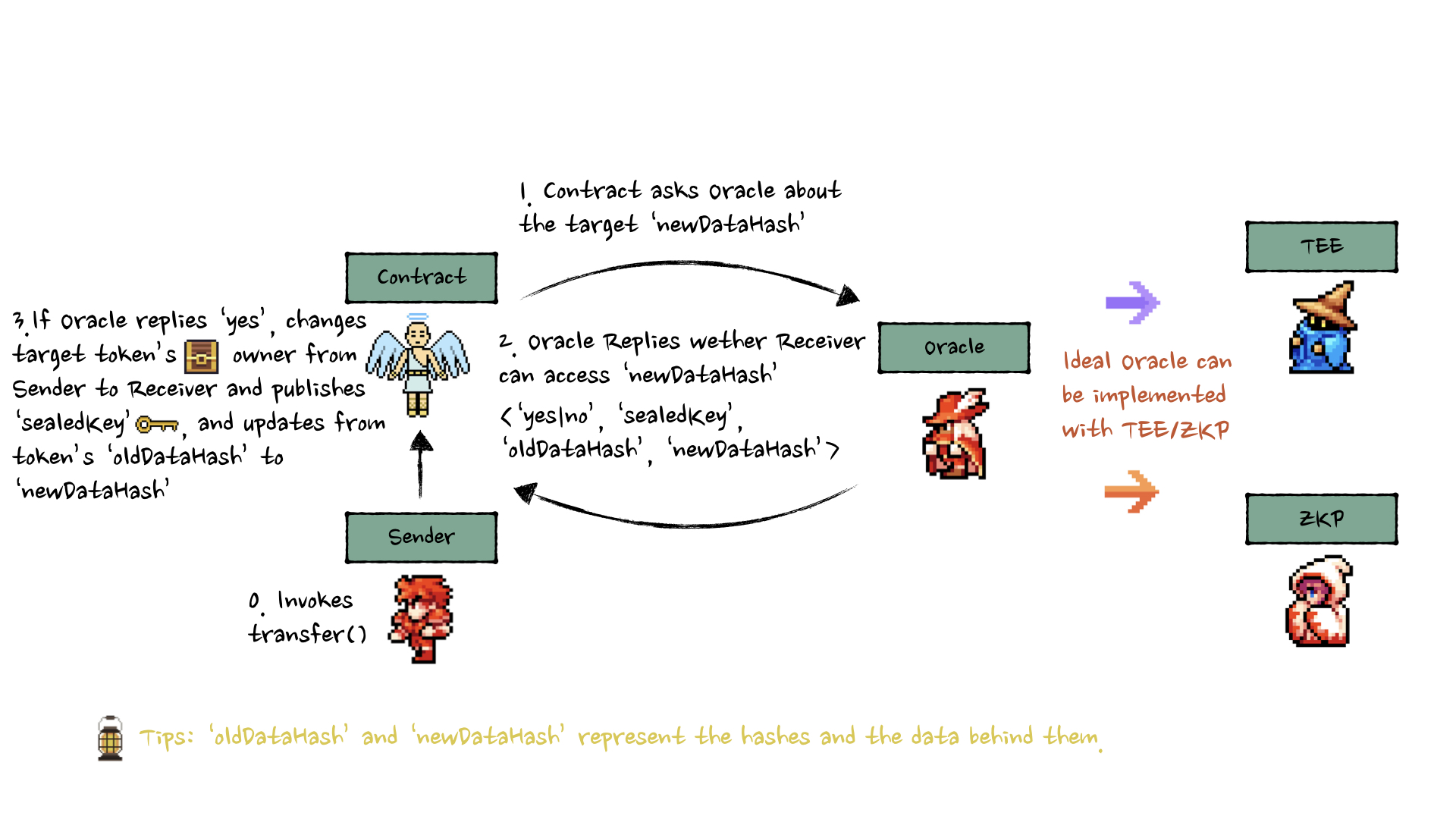
Step-by-Step Flow
1. MINT
Creator → Encrypt AI config → Store on-chain/off-chain → Mint NFT
2. USE
Owner → Decrypt config → Run AI inference → Get response
3. AUTHORIZE
Owner → Grant usage → User can use (tidak perlu transfer ownership)
4. TRANSFER
Seller → Initiate transfer → Oracle re-encrypts → Buyer receives
Interface Specification (Official)
Berikut adalah interface resmi dari 0G Agent NFT Repository:
IERC7857 Interface
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
interface IERC7857 {
/// @notice Event saat address di-approve untuk transfer token
event Approval(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/// @notice Event saat address di-approve untuk semua token
event ApprovalForAll(
address indexed _owner,
address indexed _operator,
bool _approved
);
/// @notice Event saat address di-authorize untuk menggunakan token
event Authorization(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/// @notice Event saat authorization di-revoke
event AuthorizationRevoked(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/// @notice Event saat token ditransfer
event Transferred(
uint256 _tokenId,
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to
);
/// @notice Event saat token di-clone
event Cloned(
uint256 indexed _tokenId,
uint256 indexed _newTokenId,
address _from,
address _to
);
/// @notice Event saat sealed key di-publish
event PublishedSealedKey(
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId,
bytes[] _sealedKeys
);
/// @notice Get verifier contract
function verifier() external view returns (IERC7857DataVerifier);
/// @notice Get admin address
function admin() external view returns (address);
/// @notice Set admin baru
function setAdmin(address newAdmin) external;
/// @notice Transfer dengan re-encryption proof
function iTransfer(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
TransferValidityProof[] calldata _proofs
) external;
/// @notice Clone token ke address baru
function iClone(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
TransferValidityProof[] calldata _proofs
) external returns (uint256 _newTokenId);
/// @notice Authorize user untuk menggunakan token
function authorizeUsage(uint256 _tokenId, address _user) external;
/// @notice Revoke authorization
function revokeAuthorization(uint256 _tokenId, address _user) external;
/// @notice Get token owner
function ownerOf(uint256 _tokenId) external view returns (address);
/// @notice Get authorized users
function authorizedUsersOf(uint256 _tokenId) external view returns (address[] memory);
}
IERC7857Metadata Interface
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
struct IntelligentData {
string dataDescription; // Deskripsi data
bytes32 dataHash; // Hash dari encrypted data
}
interface IERC7857Metadata {
/// @notice Get nama NFT collection
function name() external view returns (string memory);
/// @notice Get symbol NFT collection
function symbol() external view returns (string memory);
/// @notice Get intelligent data dari token
function intelligentDatasOf(uint256 _tokenId)
external view returns (IntelligentData[] memory);
}
Data Verifier Interface
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
/// @notice Tipe oracle: TEE atau ZKP
enum OracleType {
TEE,
ZKP
}
/// @notice Access proof - signature dari receiver
struct AccessProof {
bytes32 oldDataHash;
bytes32 newDataHash;
bytes nonce;
bytes encryptedPubKey;
bytes proof;
}
/// @notice Ownership proof - dari oracle (TEE/ZKP)
struct OwnershipProof {
OracleType oracleType;
bytes32 oldDataHash;
bytes32 newDataHash;
bytes sealedKey;
bytes encryptedPubKey;
bytes nonce;
bytes proof;
}
struct TransferValidityProof {
AccessProof accessProof;
OwnershipProof ownershipProof;
}
interface IERC7857DataVerifier {
/// @notice Verify transfer validity
function verifyTransferValidity(
TransferValidityProof[] calldata _proofs
) external returns (TransferValidityProofOutput[] memory);
}
Oracle Implementations
ERC-7857 mendukung dua jenis oracle untuk re-encryption:
1. TEE Implementation (Trusted Execution Environment)
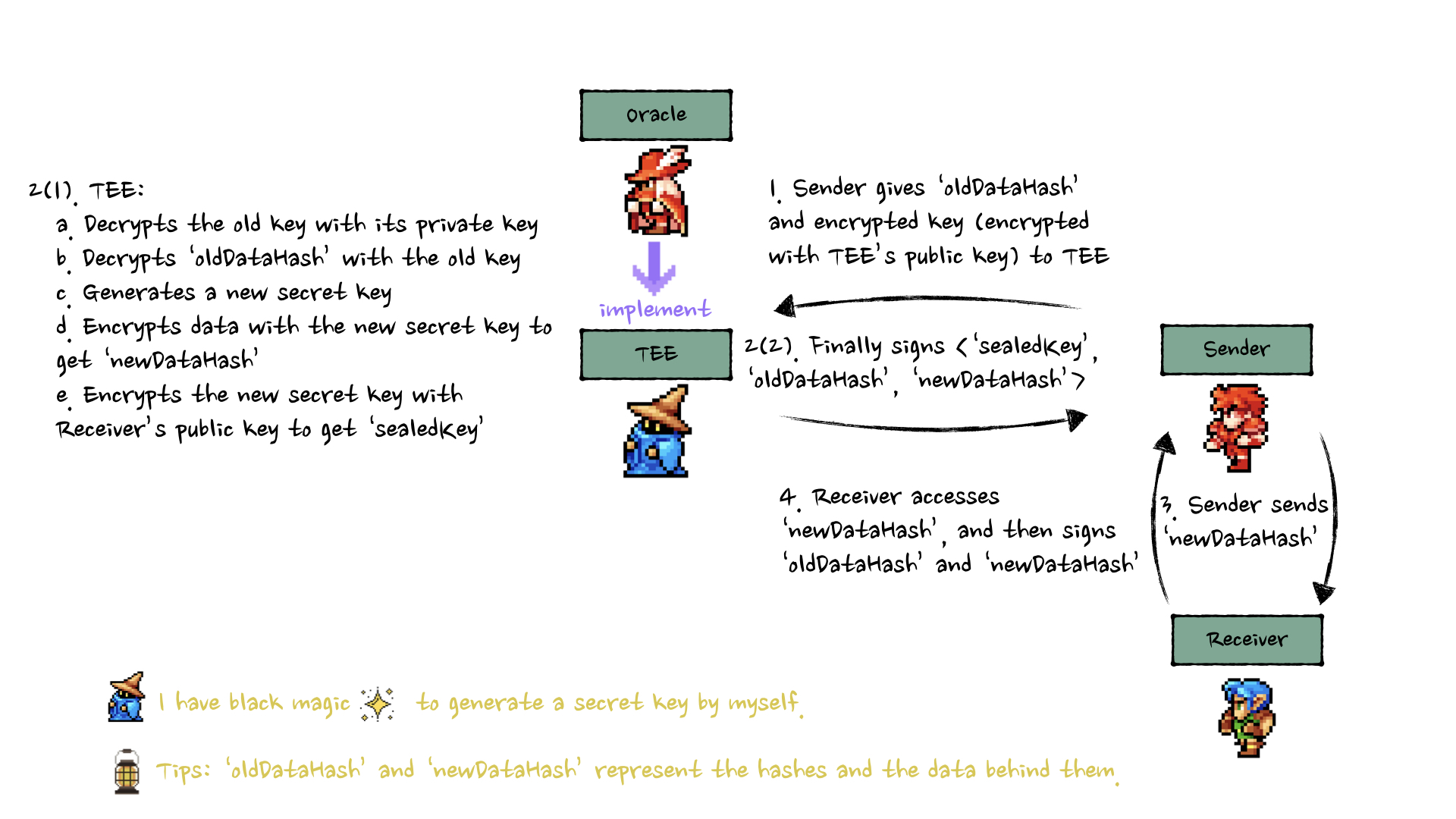
Cara Kerja TEE:
- Sender mengirim
oldDataHash, data terenkripsi, dan key ke TEE - TEE decrypt dengan private key-nya
- TEE generate new key dan re-encrypt data
- TEE output
sealedKey,oldDataHash, dannewDataHash
Keuntungan TEE:
- Hardware-level security
- Fast processing
- TEE bisa generate new key securely
Kekurangan:
- Bergantung pada hardware vendor
- Potential side-channel attacks
2. ZKP Implementation (Zero-Knowledge Proof)
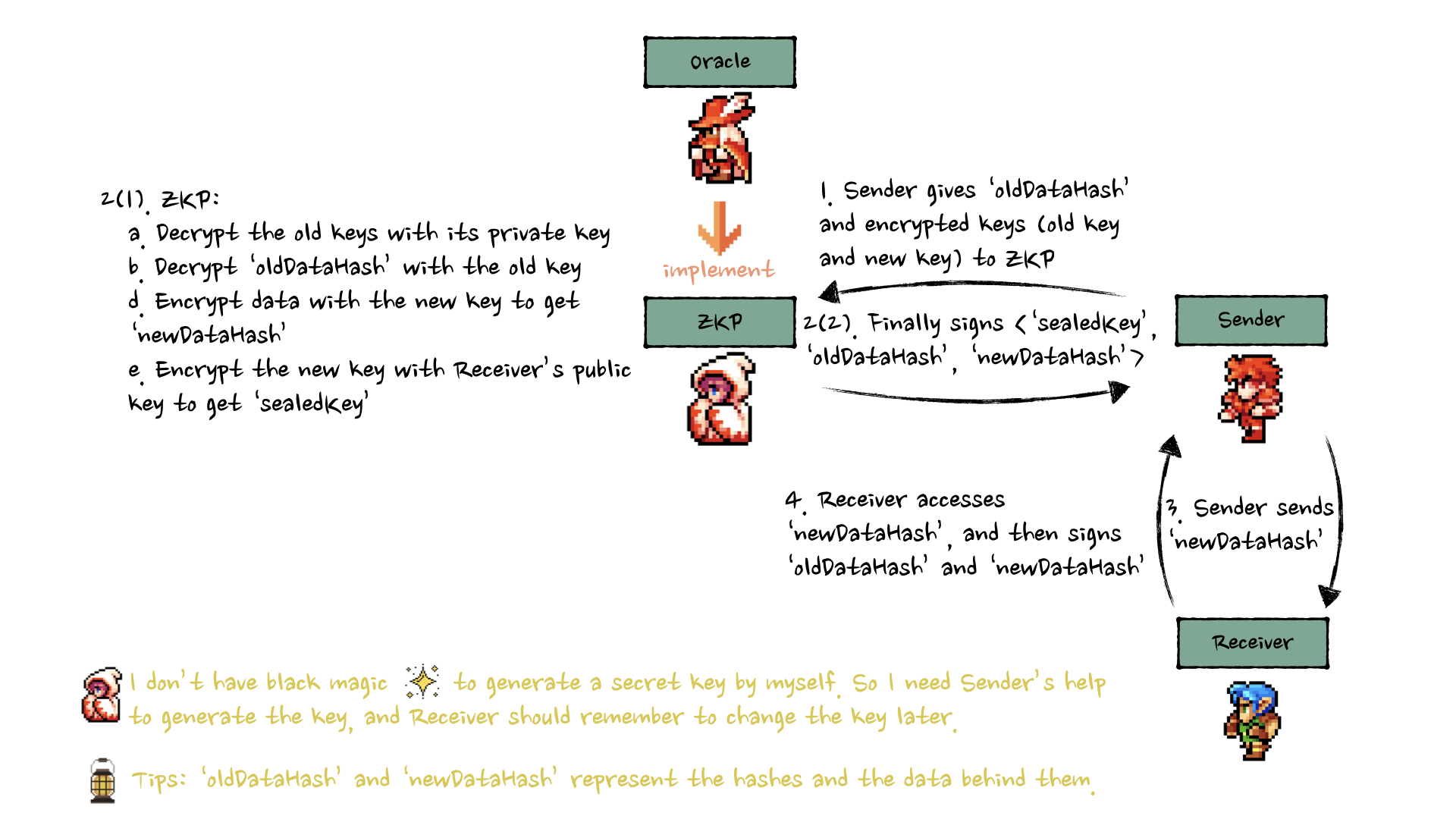
Cara Kerja ZKP:
- Generate proof bahwa re-encryption valid
- Verifier confirm proof tanpa melihat data asli
- Smart contract verify proof on-chain
Keuntungan ZKP:
- Trustless (no trusted third party)
- Mathematically provable security
- Fully decentralized
Kekurangan:
- Receiver harus ganti key saat update berikutnya
- Computationally expensive
Perbandingan TEE vs ZKP
| Aspek | TEE | ZKP |
|---|---|---|
| Trust Model | Hardware vendor | Math |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Key Generation | Secure new key | Receiver must change |
| Decentralization | Partial | Full |
| Best For | High throughput | Maximum trust |
Full Flow
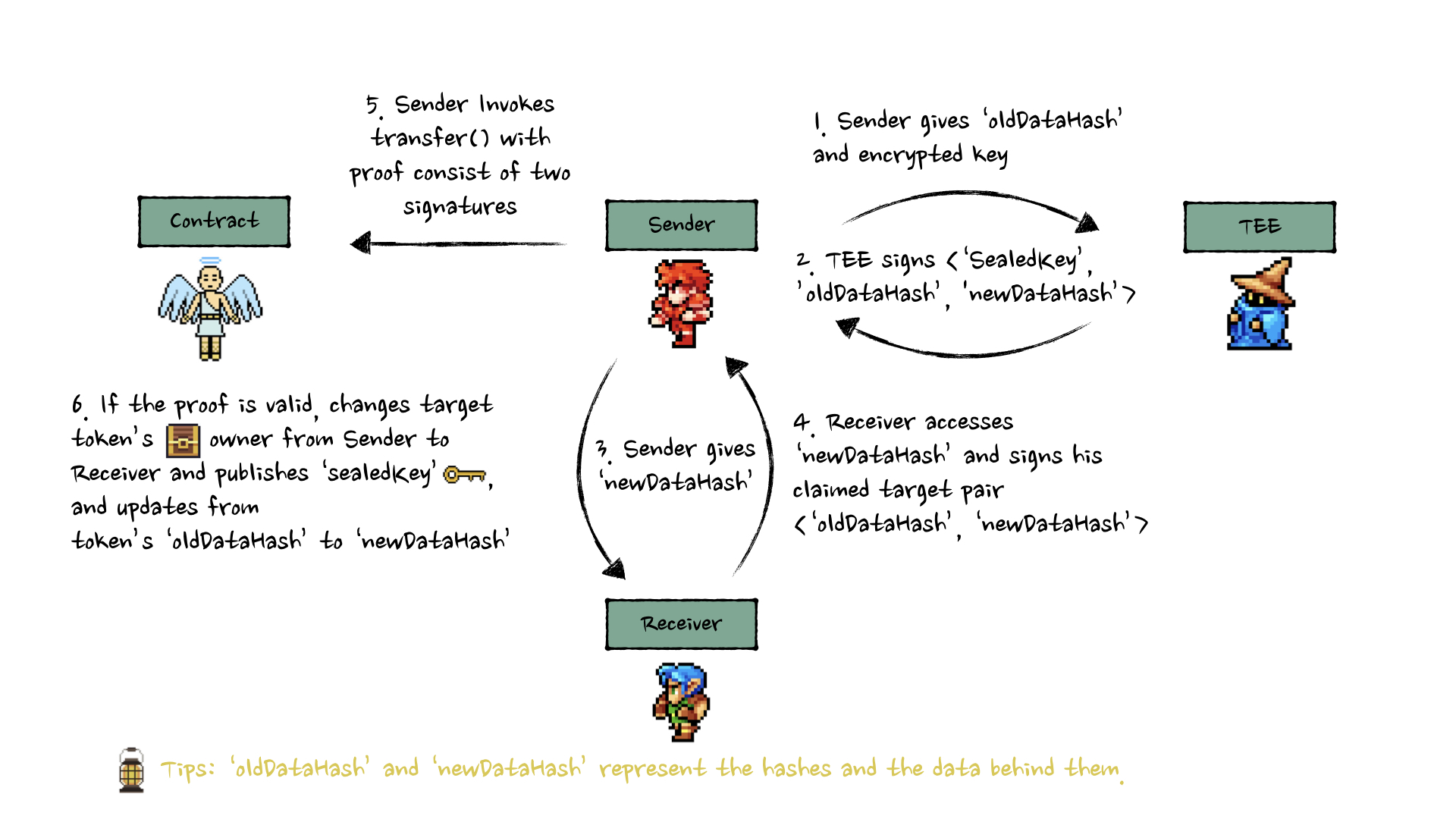
Alur lengkap transfer:
- Sender interaksi dengan TEE/ZKP untuk dapat signature verifikasi
- Sender minta signature dari Receiver untuk konfirmasi akses
- Sender submit kedua signature ke
transfer() - Contract verify signatures dan update state
- Receiver decrypt data dengan key dari
sealedKey
AgentNFT Contract
Implementasi lengkap ERC-7857 di 0G:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract AgentNFT is
AccessControlUpgradeable,
ReentrancyGuardUpgradeable,
PausableUpgradeable,
IERC7857,
IERC7857Metadata
{
struct TokenData {
address owner;
address[] authorizedUsers;
address approvedUser;
IntelligentData[] iDatas;
}
uint256 public constant MAX_AUTHORIZED_USERS = 100;
// Mint INFT baru
function mint(
IntelligentData[] calldata iDatas,
address to
) public payable virtual returns (uint256 tokenId);
// Transfer dengan proof
function iTransfer(
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
TransferValidityProof[] calldata proofs
) public virtual;
// Clone token
function iClone(
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
TransferValidityProof[] calldata proofs
) public virtual returns (uint256);
// Authorize user untuk menggunakan token
function authorizeUsage(uint256 tokenId, address to) public virtual;
// Batch authorize multiple users
function batchAuthorizeUsage(
uint256 tokenId,
address[] calldata users
) public virtual;
// Revoke authorization
function revokeAuthorization(uint256 tokenId, address user) public virtual;
// Clear semua authorized users
function clearAuthorizedUsers(uint256 tokenId) public virtual;
// Get authorized users
function authorizedUsersOf(uint256 tokenId)
public view virtual returns (address[] memory);
// Get intelligent data
function intelligentDatasOf(uint256 tokenId)
public view virtual returns (IntelligentData[] memory);
}
Key Functions Explained
1. mint() - Membuat INFT Baru
function mint(
IntelligentData[] calldata iDatas,
address to
) public payable returns (uint256 tokenId) {
require(to != address(0), "Zero address");
require(iDatas.length > 0, "Empty data array");
tokenId = nextTokenId++;
tokens[tokenId].owner = to;
for (uint i = 0; i < iDatas.length; i++) {
tokens[tokenId].iDatas.push(iDatas[i]);
}
emit Minted(tokenId, msg.sender, to);
}
2. authorizeUsage() - Grant Usage Rights
function authorizeUsage(uint256 tokenId, address to) public {
require(to != address(0), "Zero address");
require(tokens[tokenId].owner == msg.sender, "Not owner");
require(
tokens[tokenId].authorizedUsers.length < MAX_AUTHORIZED_USERS,
"Too many authorized users"
);
tokens[tokenId].authorizedUsers.push(to);
emit Authorization(msg.sender, to, tokenId);
}
3. revokeAuthorization() - Revoke Usage Rights
function revokeAuthorization(uint256 tokenId, address user) public {
require(tokens[tokenId].owner == msg.sender, "Not owner");
address[] storage authorizedUsers = tokens[tokenId].authorizedUsers;
for (uint i = 0; i < authorizedUsers.length; i++) {
if (authorizedUsers[i] == user) {
authorizedUsers[i] = authorizedUsers[authorizedUsers.length - 1];
authorizedUsers.pop();
break;
}
}
emit AuthorizationRevoked(msg.sender, user, tokenId);
}
Security Considerations
1. Key Management
- Private keys HARUS aman
- Gunakan hardware wallet untuk high-value INFTs
- Backup encrypted, bukan plaintext
2. Oracle Trust
- Pilih oracle implementation sesuai kebutuhan
- TEE untuk speed, ZKP untuk trustlessness
3. Authorization Limits
- Max 100 authorized users per token
- Revoke yang tidak digunakan
- Monitor usage patterns
Summary
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| IntelligentData | Store encrypted AI config hash |
| TransferValidityProof | Verify re-encryption on transfer |
| authorizeUsage | Grant usage without ownership transfer |
| Oracle (TEE/ZKP) | Secure re-encryption mechanism |
Lanjut ke Implementasi
Sekarang kamu sudah paham standard ERC-7857, lanjut ke Integration Guide untuk mulai coding dengan contract resmi!